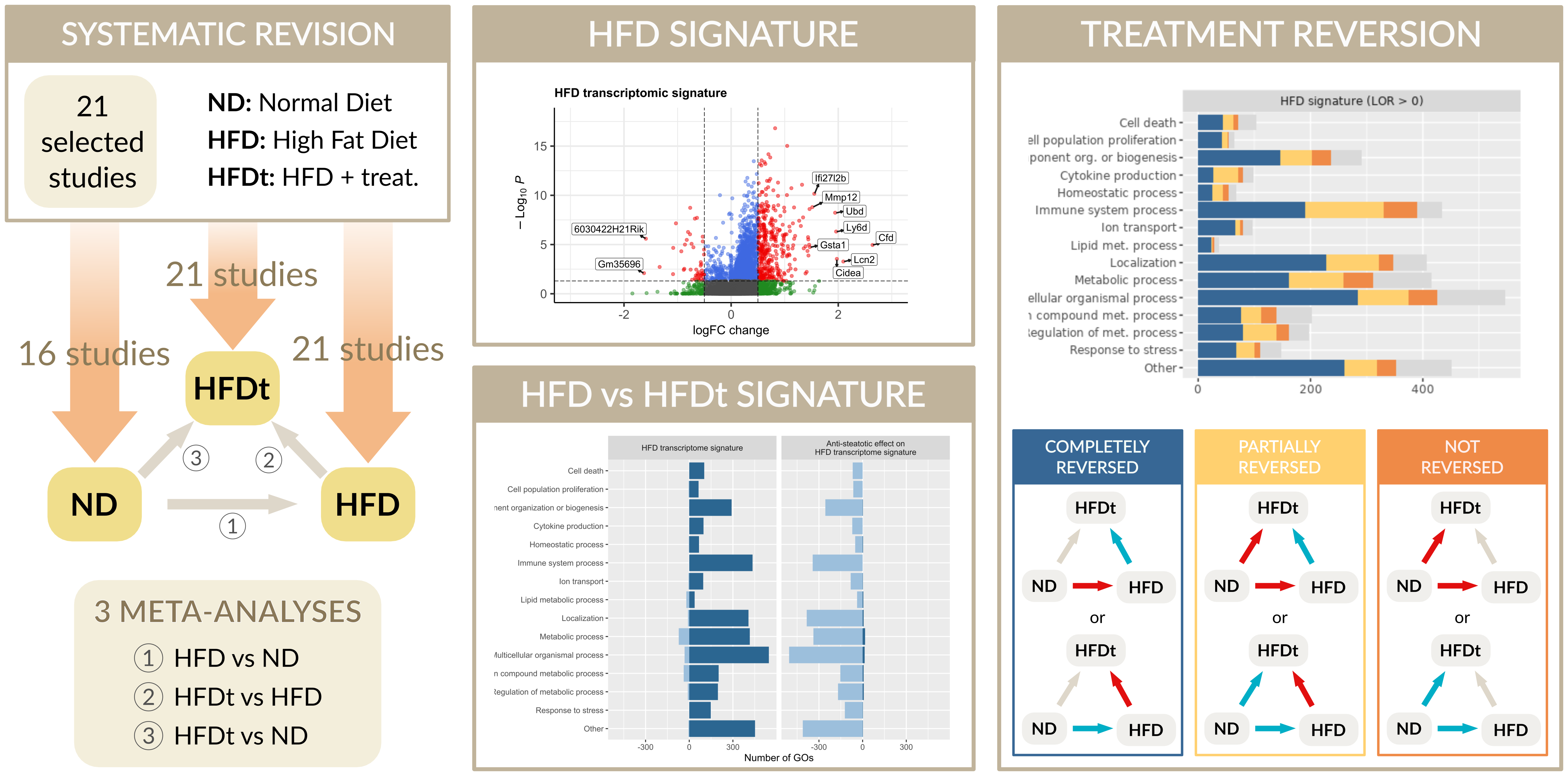
Graphical abstract. We carried out a systematic review
in GEO database for transcriptomic studies comparing the hepatic gene expression of wild type HFD-fed C57BL6/J
mice with that of control mice (normal diet, ND), and that of HFD-fed mice receiving potential anti-steatotic
treatments. After performing a differential gene expression analysis, we conducted a meta-analysis to define
the hepatic gene expression signature of HFD mice. We also evaluated the capacity of the anti-steatotic treatments
to modulate this transcriptomic signature.
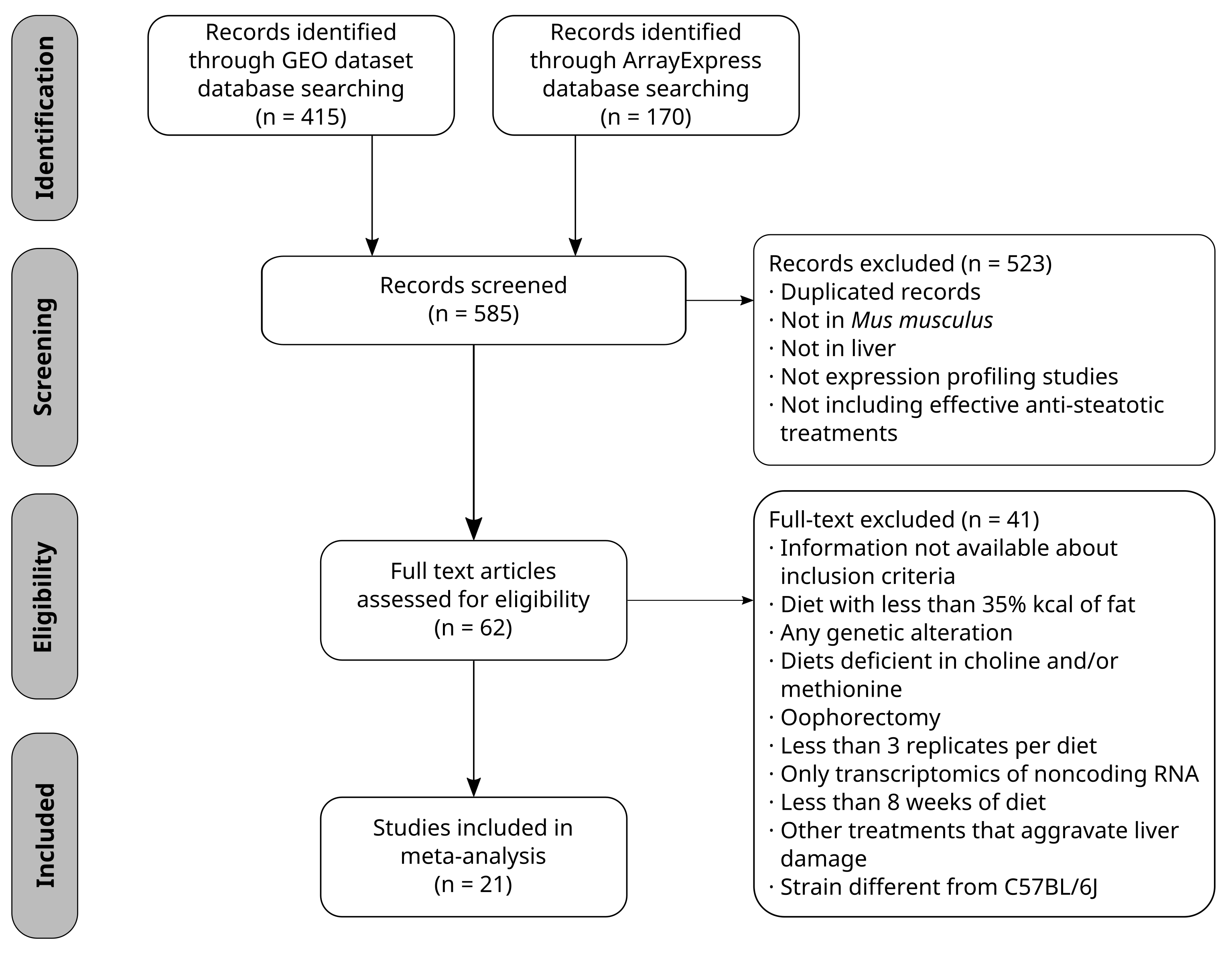
In the systematic review, 21 selected studies were finally
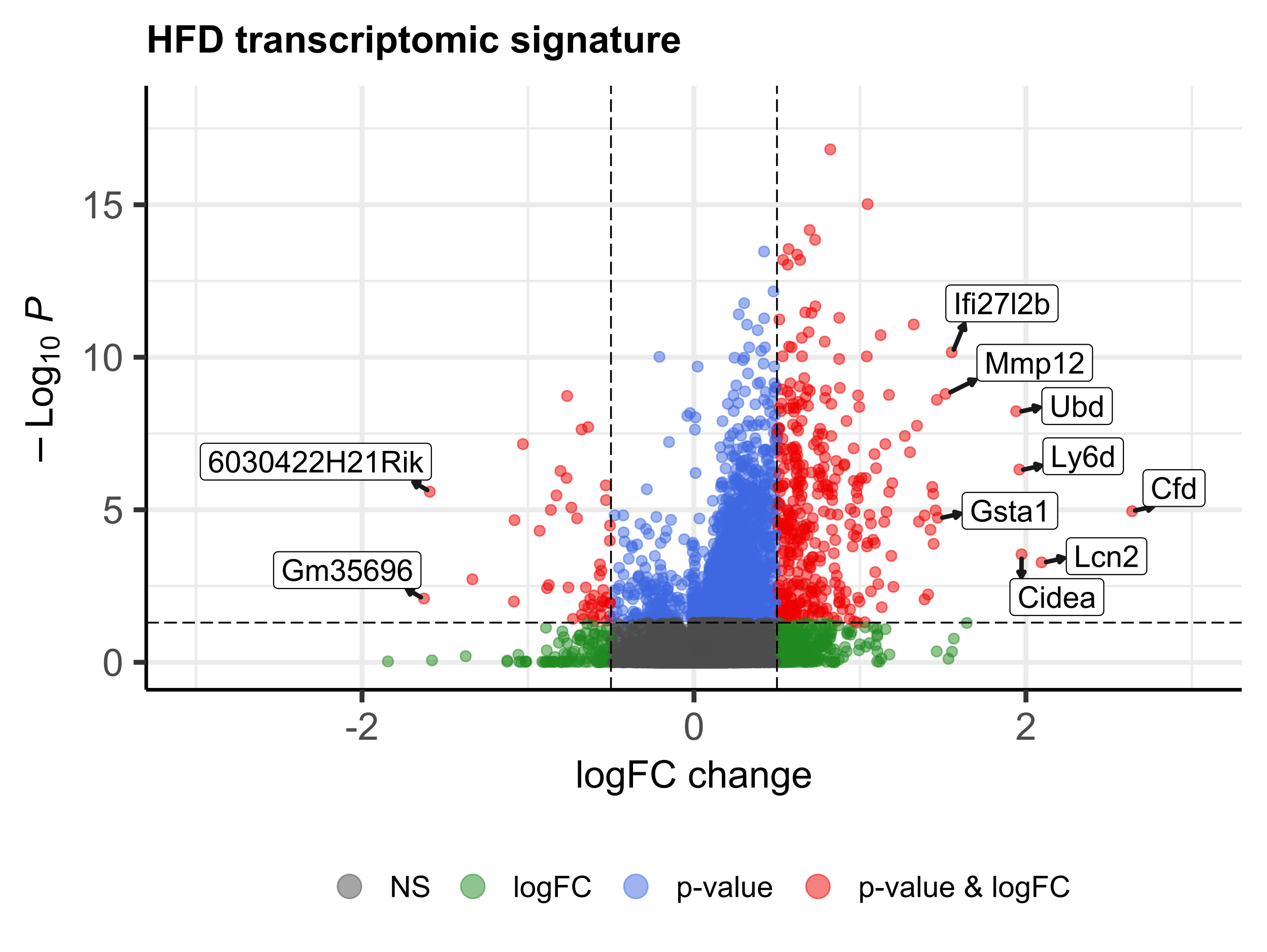
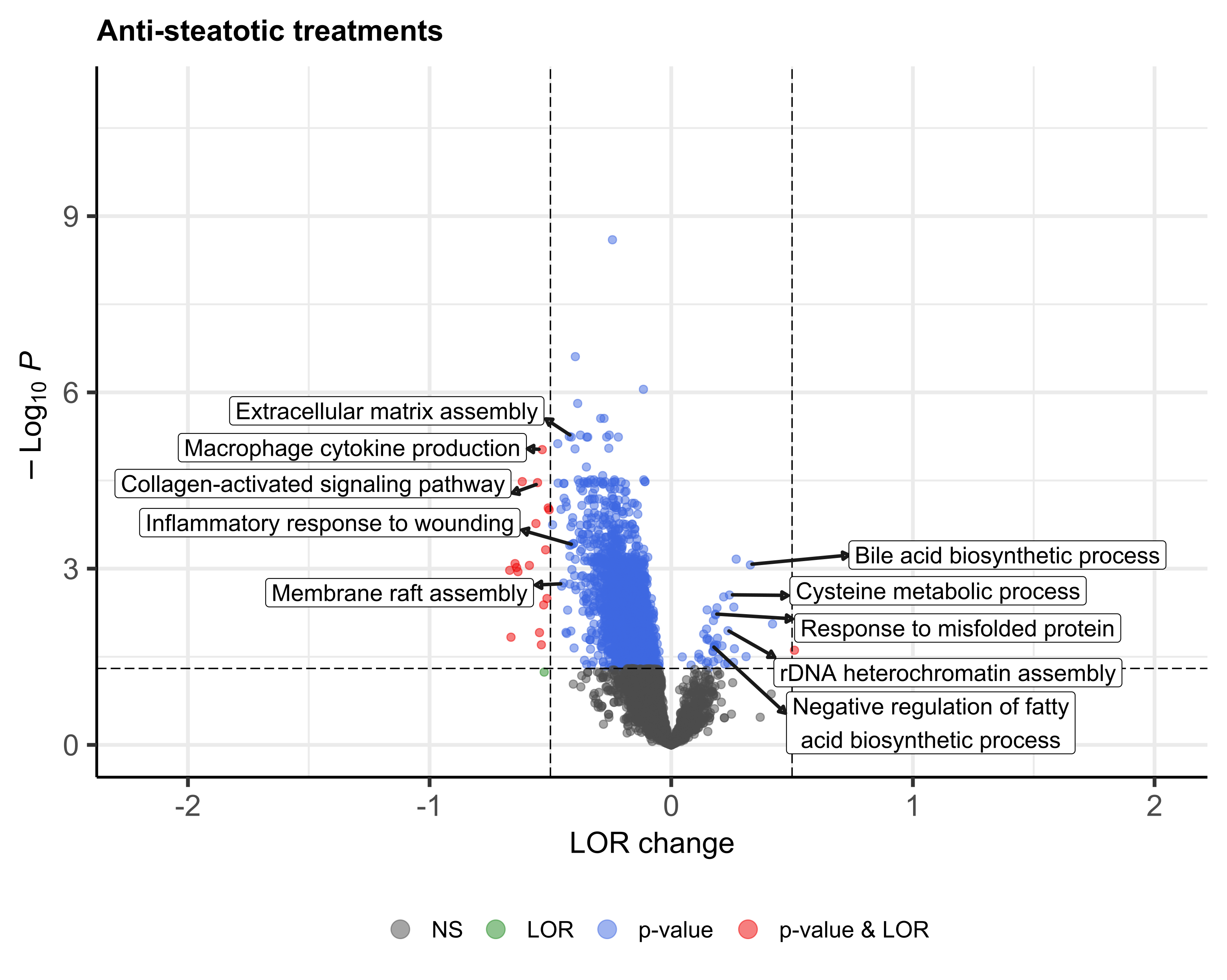
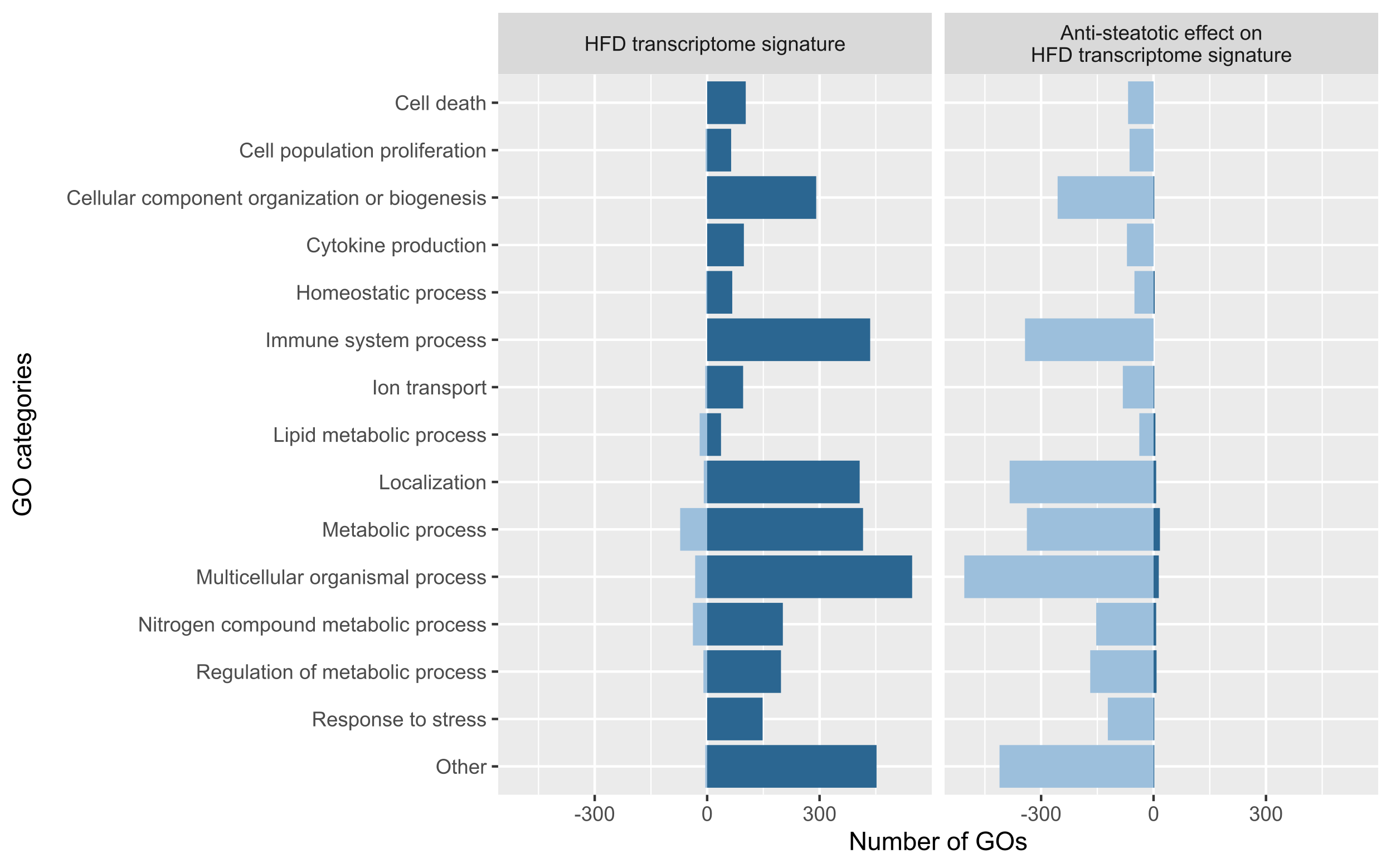
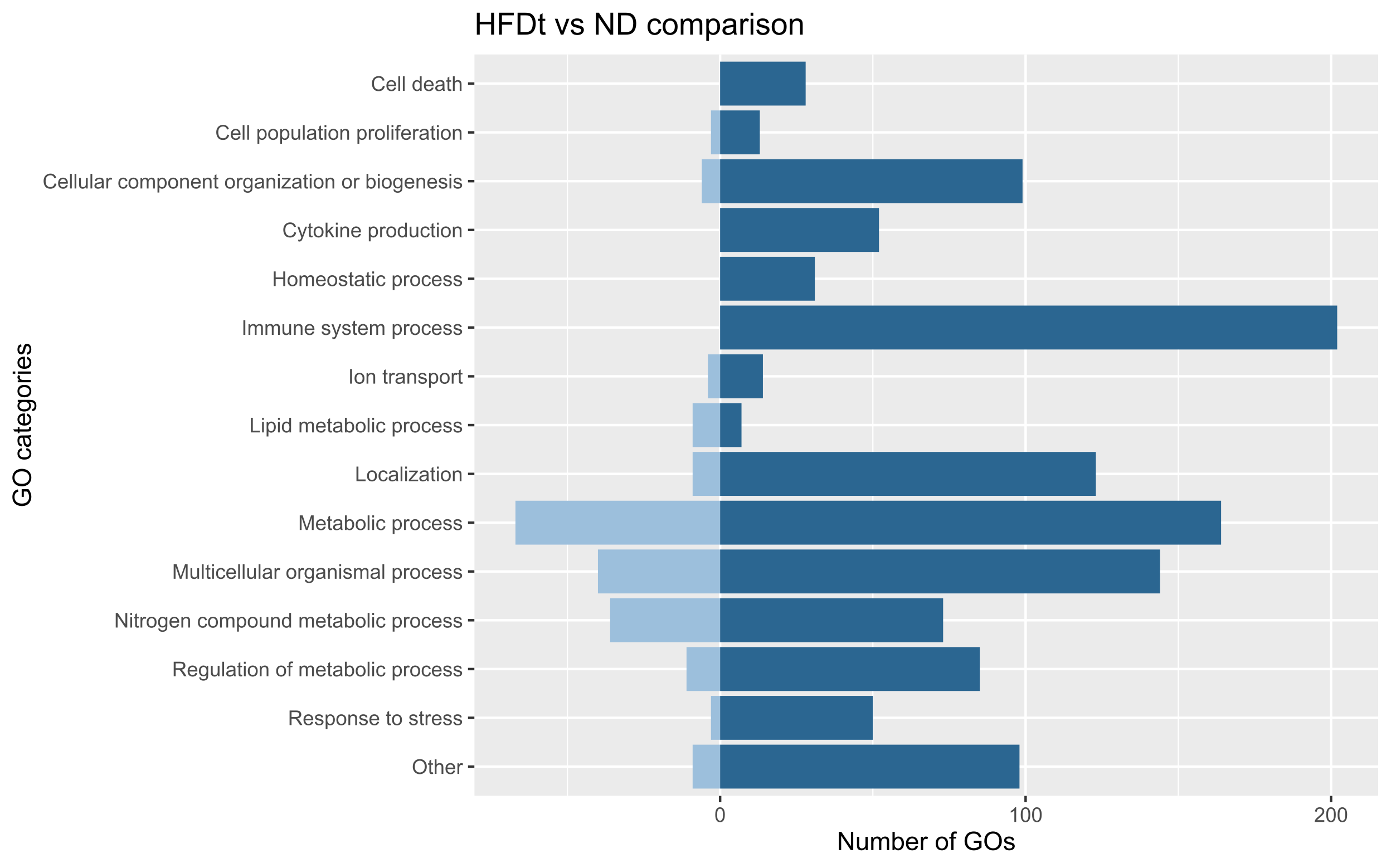
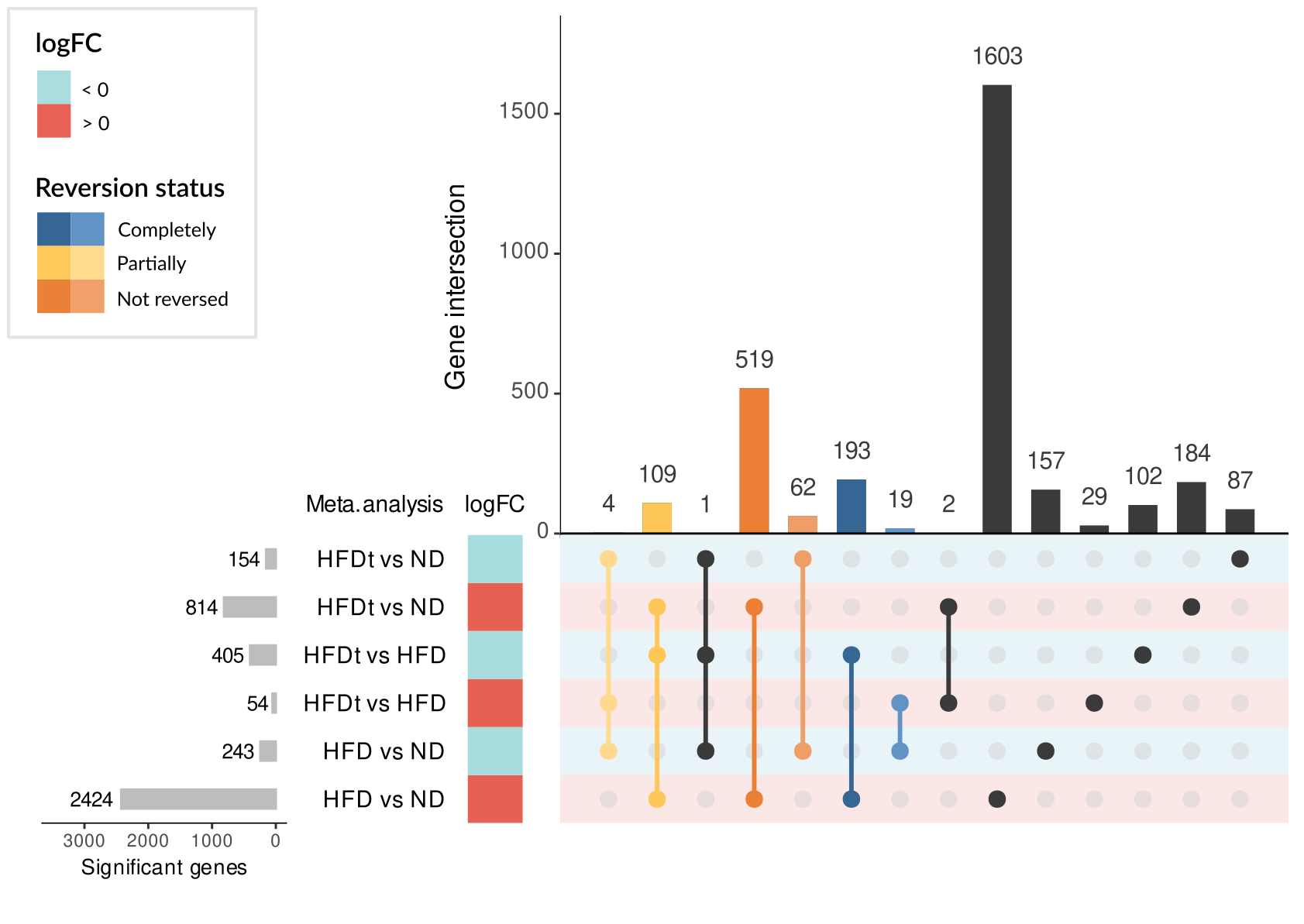
analysed, which included 22 different treatments. We obtained a transcriptomic signature of HFD murine models
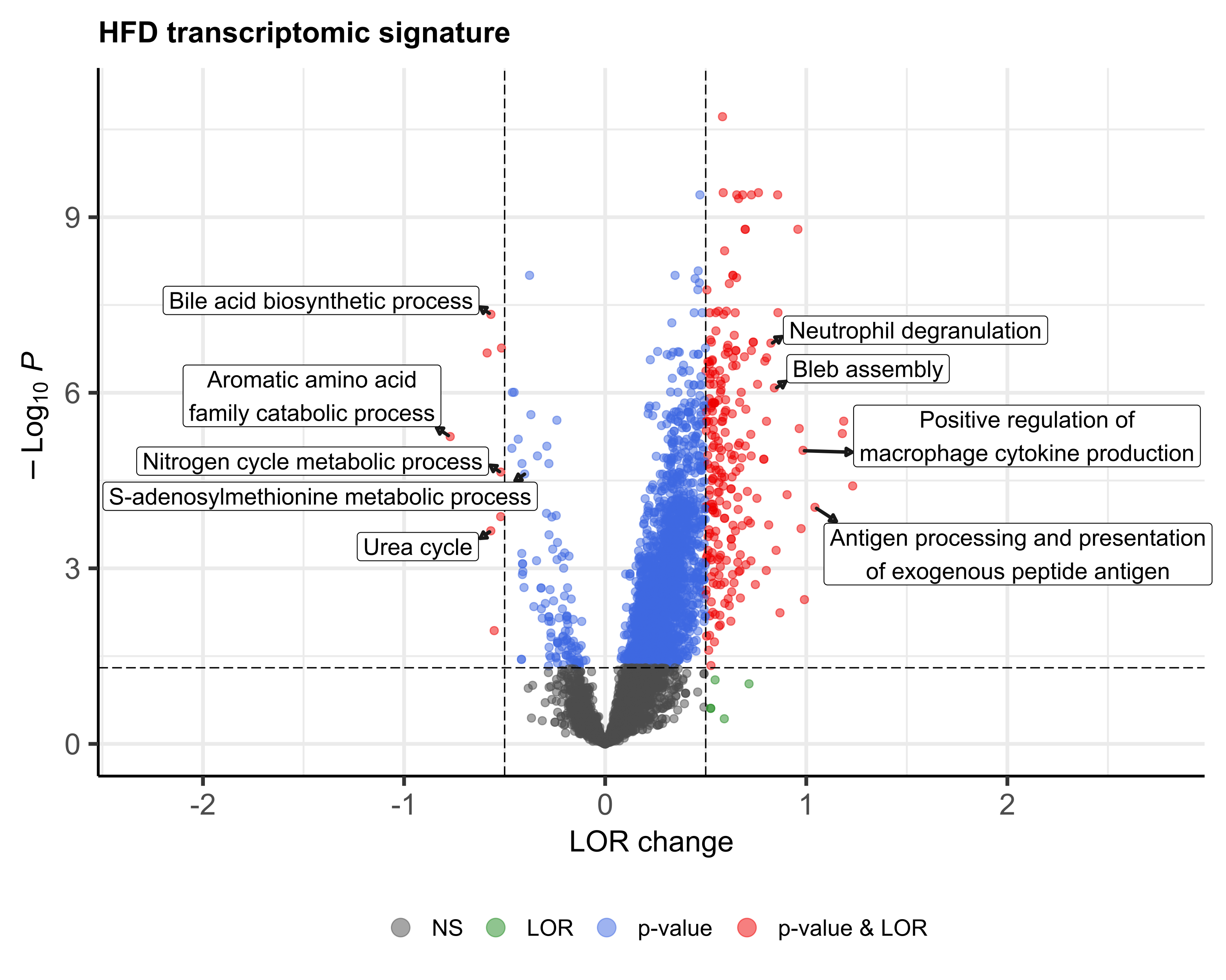
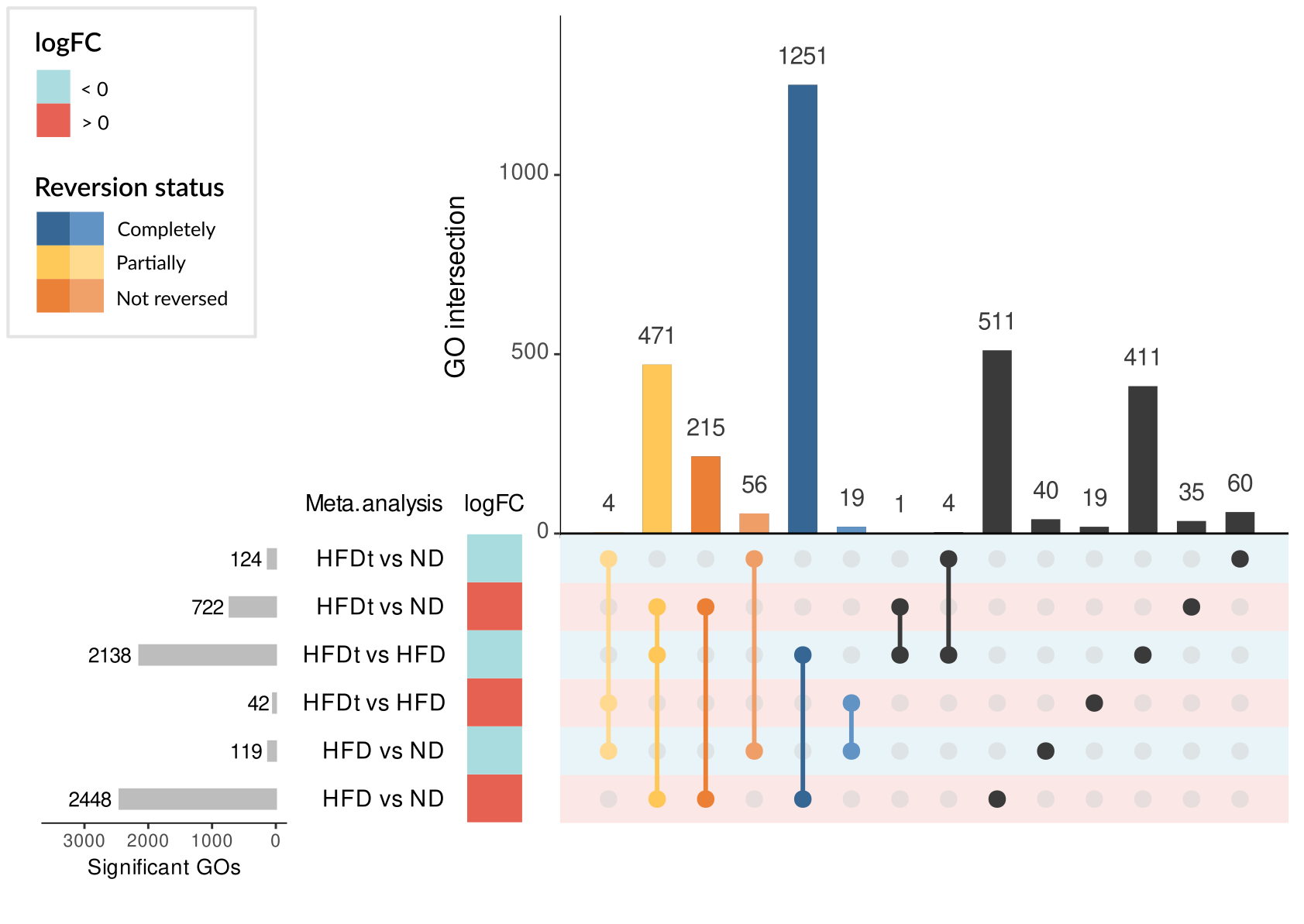
containing 2670 genes and, at the functional level, 2567 GO biological processes altered, most of them involved
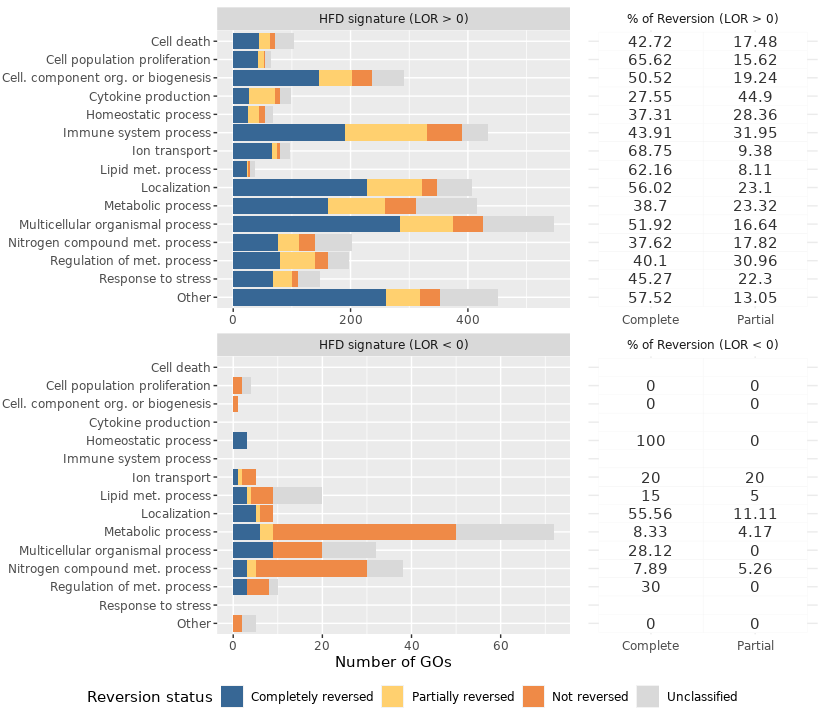
in immune response, cell death, response to stress, cell cycle and metabolism. Generally, treated HFD-mice
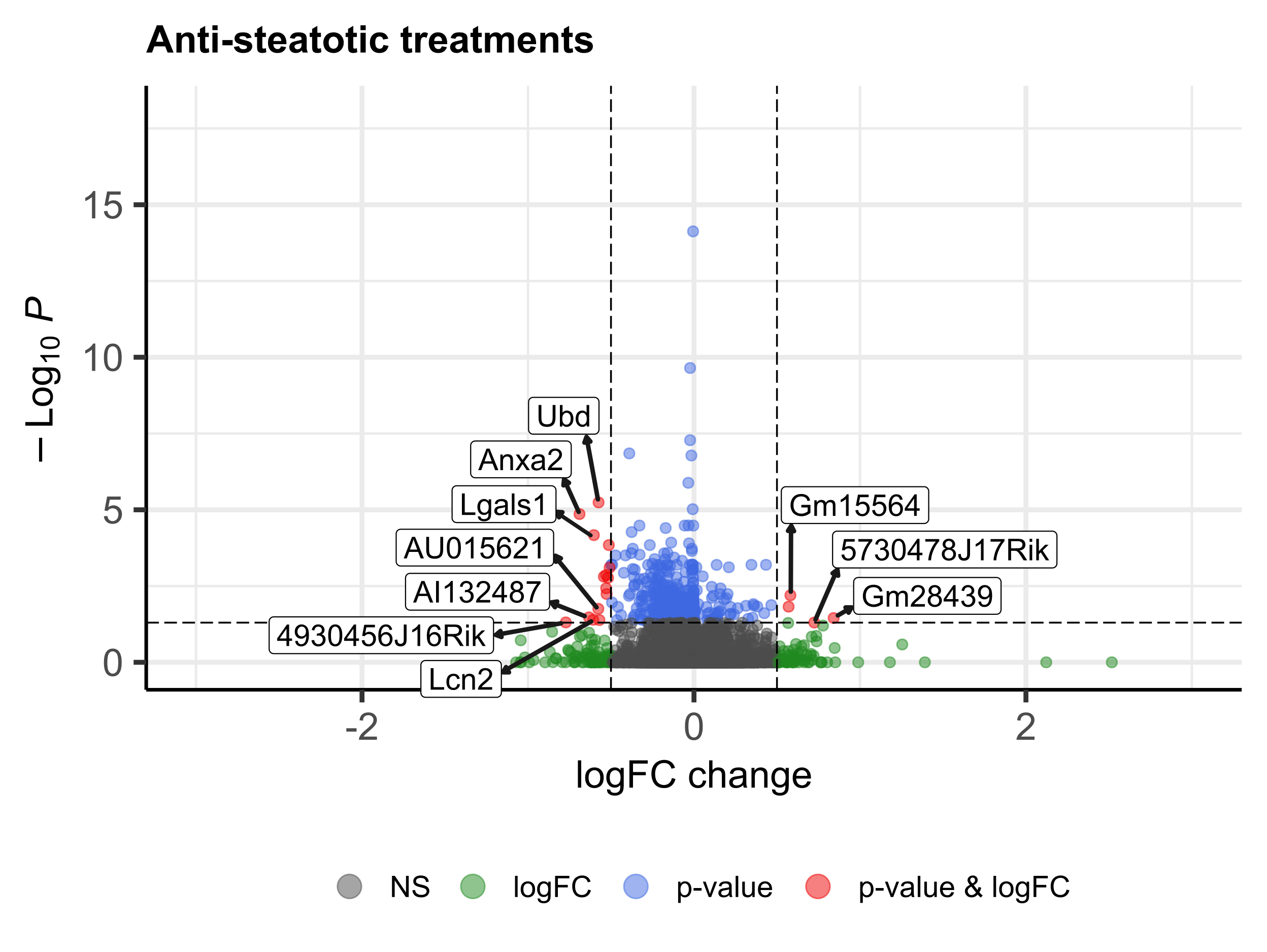
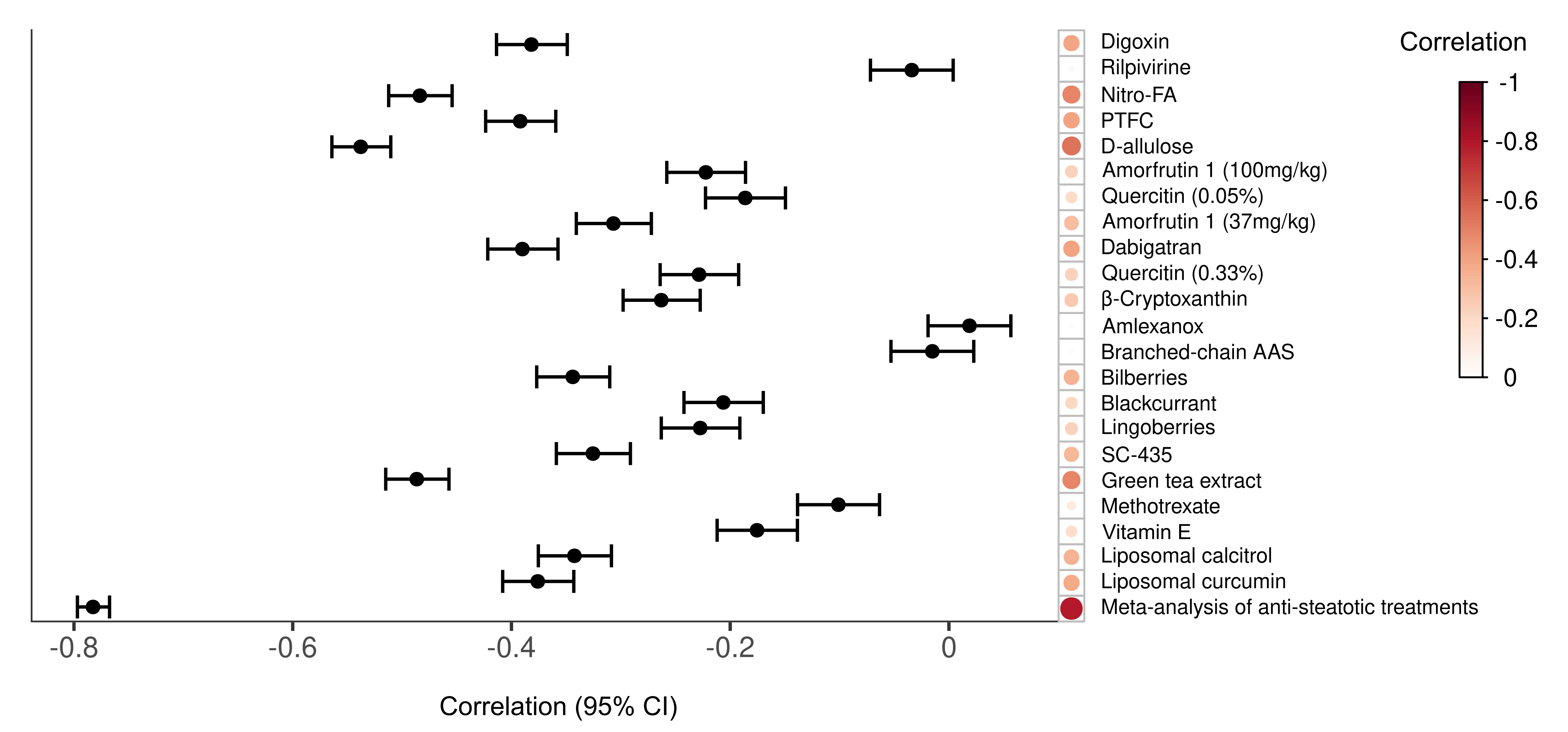
showed a reversion of this HFD signature, although to different extent depending on the treatment. Among the
genes of the HFD signature, we identified 325 genes whose expression was commonly reversed by treatments and
581 whose expression was not reversed. Regarding GO terms of the HFD signature, 1745 were reversed and 271 were
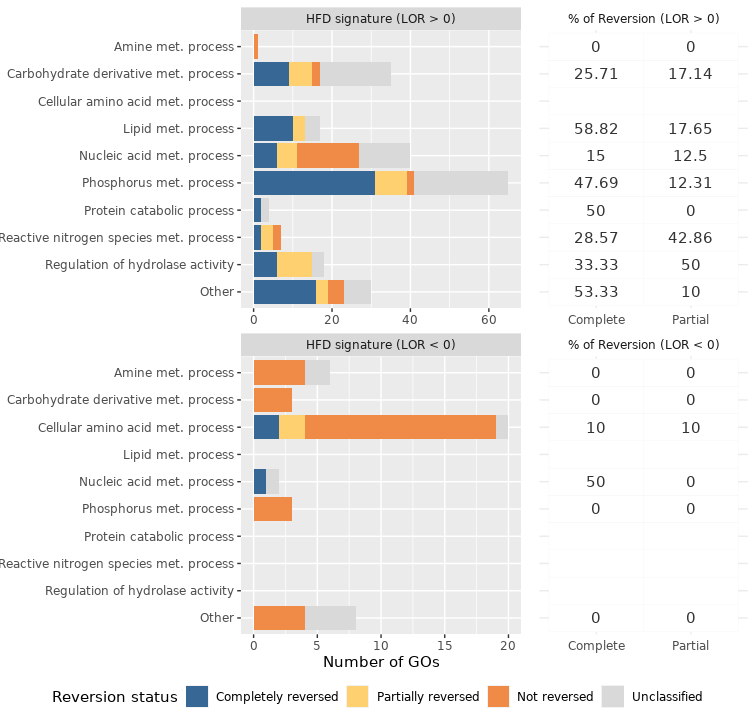
not. The biological processes most frequently reversed were those related to lipid metabolism, cell death, cell
proliferation, response to stress and immune system process. Conversely, processes related to nitrogen compound
metabolism were usually not reversed. Comparing our HFD signature with a human NAFLD progression signature, we
identified 62 common genes: 10 of them were of those generally reversed by treatments and 12 belong to the not
reversed group.
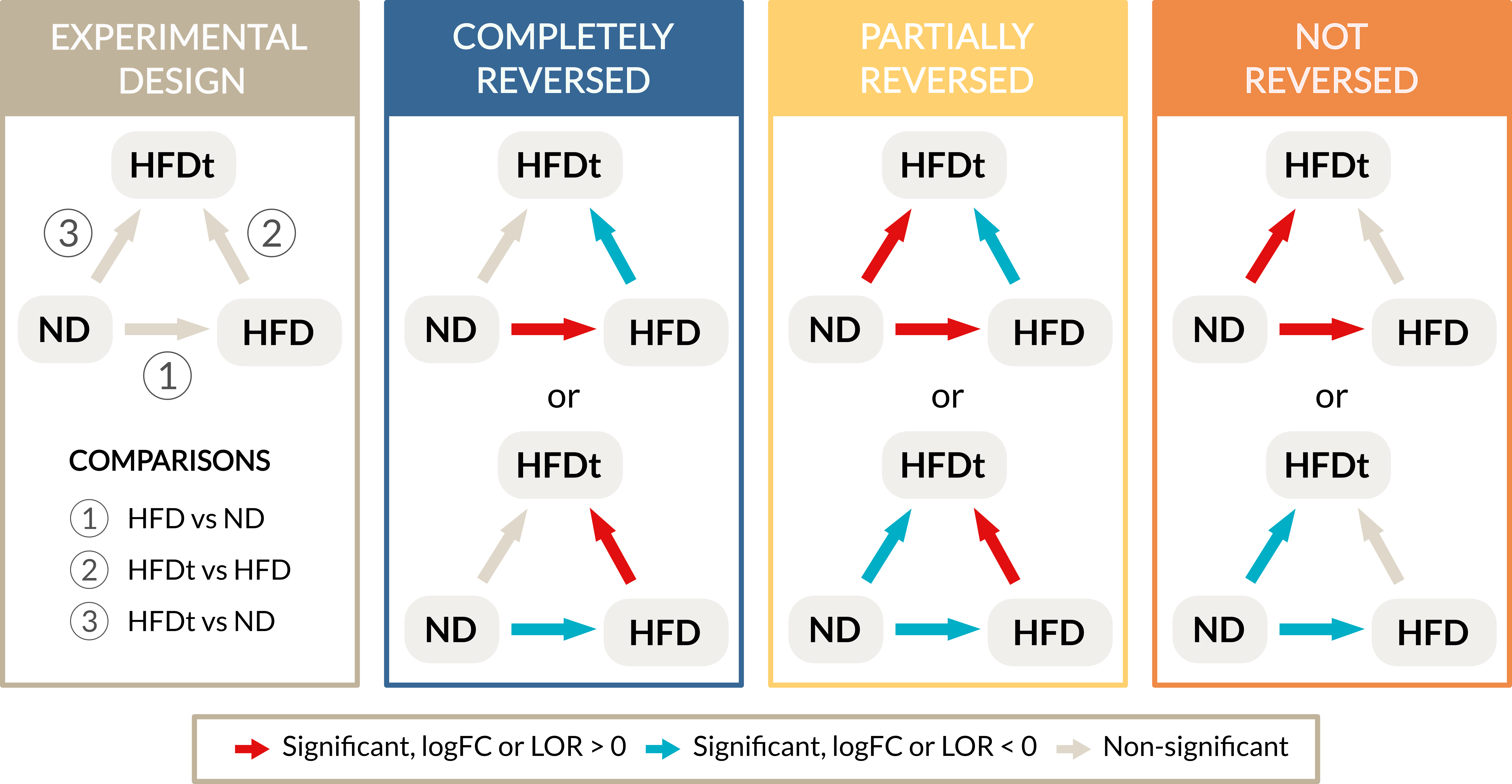
Graphical representation of the inclusion criteria for reversal definitions. The comparisons
are numbered from 1 to 3, the groups are normal diet (ND), high fat diet (HFD) and high fat diet with treatment (HFDt).
Colors represent the direction of change, being red up-regulation and blue down-regulation.
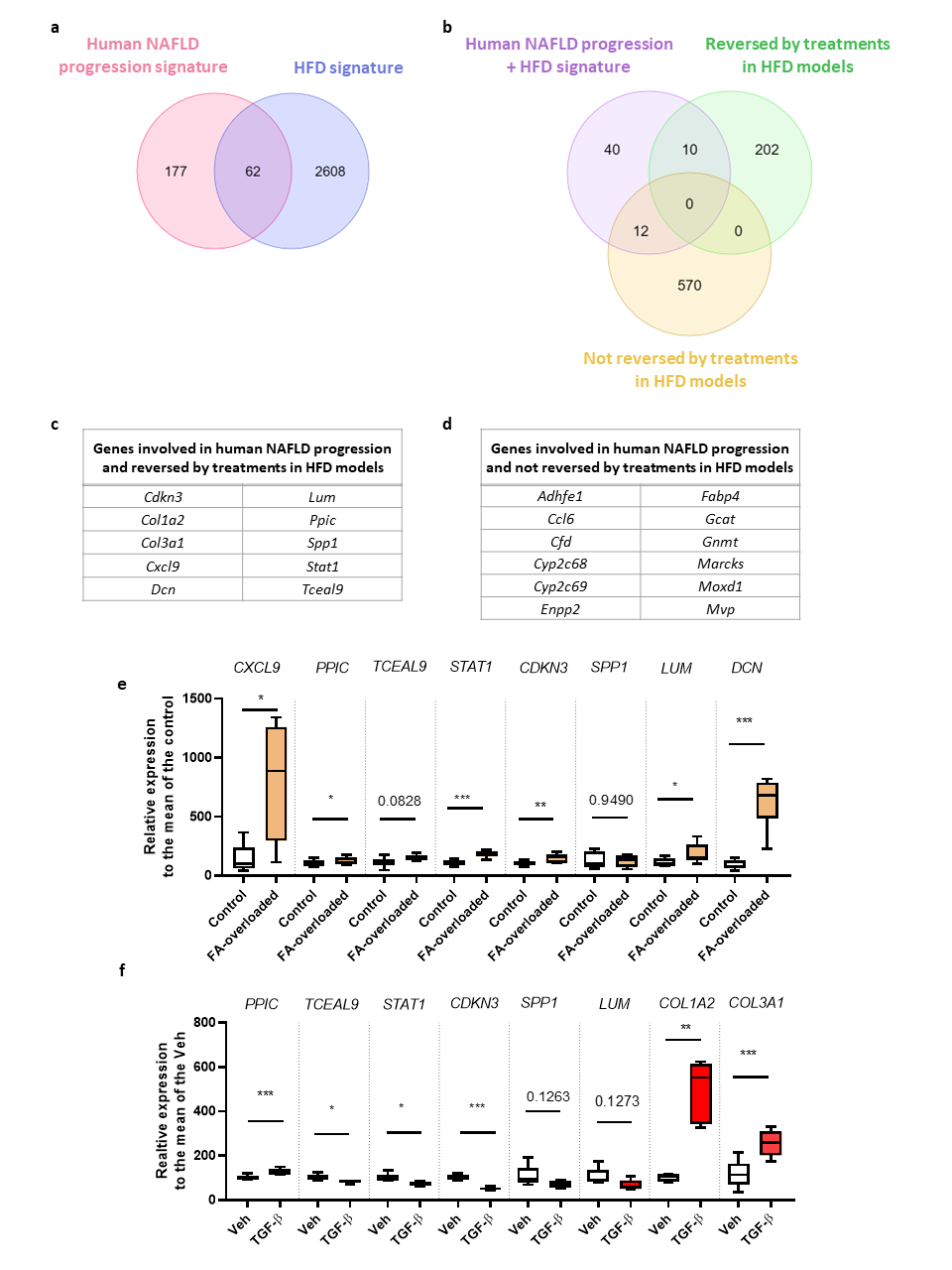
Comparison between HFD murine model and human NAFLD progression signature. a)
Venn diagram comparing the HFD mouse model transcriptomic signature with a human NAFLD progression transcriptomic
signature from the literature. b) Venn diagram comparing the 62 common genes between human NAFLD progression
and HFD mouse model transcriptomic signatures with those whose expression was reversed or not by the anti-steatotic
treatments in HFD mouse models according to our meta-analysis. c-d) Common genes between human NAFLD progression
and HFD mouse model transcriptomic signatures whose expression was reversed (c) or not (d) by the treatments.
e-f) Validation of gene expression in in vitro models of human hepatocytes overloaded with fatty acids
(FA-overloaded) (e) and human profibrogenic hepatic stellate cells (treated with TGF-β) (f) for those candidate
genes whose expression was reversed by treatments. Data were analysed by a paired t test (*p-value > 0.05,
**p-value > 0.01, ***p-value > 0.001).
Phenotypic characteristics of HFD murine model
Available data on the metabolic and hepatic changes induced by the different high fat diet mouse models employed in the meta-analysis| Article (PMID) | n | Age (weeks) | Diet contributors to liver damage | HFD (weeks) | Sex | Phenotypic characteristics of HFD murine model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight gain | Insulin resistance | Technique / Parameter | Inflammation | Technique / Parameter | Liver fibrosis | Technique / Parameter | ||||||
Phenotypic characteristics of HFD murine model after treatments
Available data on the metabolic and hepatic changes induced by each of the anti-steatotic treatment studied in the meta-analysis.| Article (PMID) | Treatment | Dose | Phenotypic characteristics of HFD murine model after treatments | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss | Improvement in IR | Technique / Parameter | Anti-steatotic effect | Technique / Parameter | Anti-inflammatory effect | Technique / Parameter | Anti-fibrotic effect | Technique / Parameter | |||